Original Peng Min Phoenix Network Reading
Peng Min, born in Hengyang, Hunan Province in 1983, graduated from the Chinese Department of Peking University with a master’s degree and is now the deputy director of the editorial department of Poetry Magazine. He has won the annual newcomer award for short stories in people’s literature, the champion of the 2nd China Idiom Conference of CCTV and the champion of the 5th Chinese Poetry Conference. Run WeChat official account "Peng Min Xian Sen".
Qingping music, once a word brand, has now become a title of the play. I don’t know if the play is good or not, but the nine-year compulsory education in which people collectively appeared recited the men’s day group, but it made people feel a little "nightmare reliving". Today, we will talk about these great gods.
01
Seven-year-old Yan Shu who "sings the Phoenix"
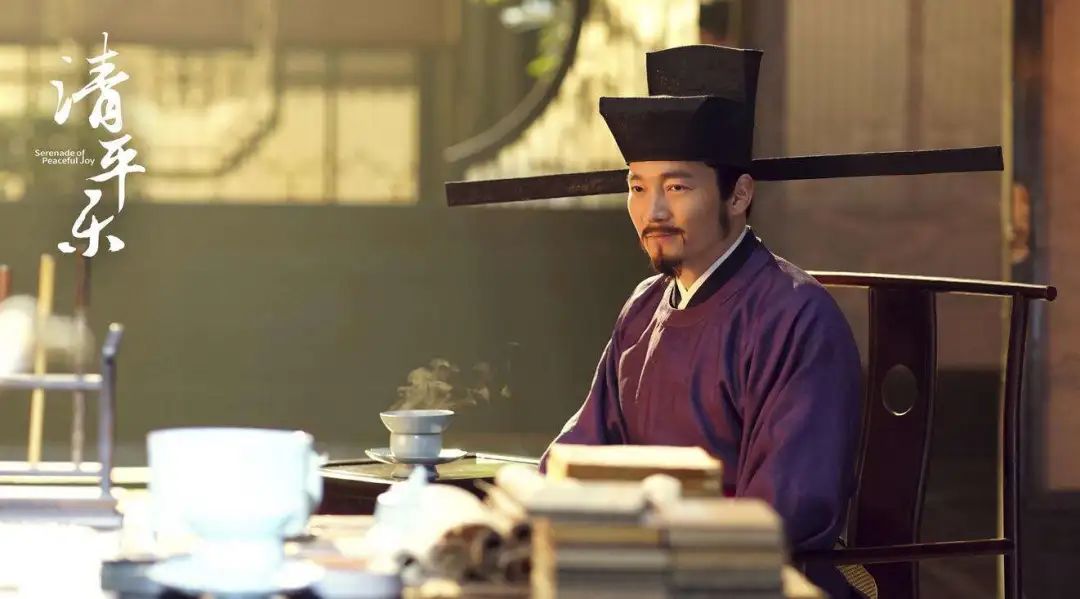
As we all know, the Song Dynasty valued literature over martial arts and was a paradise for literati. Many famous literati are also high-ranking officials and officials, and they are winners in life. Among them, Yan Shu, the prime minister poet, is the most enviable one.
Yan Shu, stills of Qingpingle.
Yan Shu’s starting line is not high, and his father is just a small jailer. It’s a mystery how this ordinary grass-roots civil servant managed prisoners, and how he cultivated a literary giant with a long history, and at the same time, he was a powerful prime minister.
At an early age, Yan Shu showed extraordinary signs. In view of the fact that Luo Binwang wrote Ode to Goose at the age of seven, Du Fu was able to "sing to the phoenix" at the age of seven, and Yan Shu, a child prodigy, was unwilling to lag behind, and also started his brilliant literary career at the age of seven, and his wonderful pen gave birth to hundreds of flowers.
At the age of fourteen, the prodigy’s talent finally shocked the imperial court, and he was brought to Beijing as a god-class local product by local officials, and took part in the imperial examination with more than 1000 adult candidates.
The initial trial went quite smoothly, and the big brothers and sisters next to him were still scratching their heads. Yan Shu had "helped others to write". However, there was a little problem in the second interview two days later.
One of the links in the second interview is to create a propositional composition, but when the examination paper was handed out, Yan Shu froze. This topic happened to be written by him before. If the finished product is directly copied to the answer sheet, isn’t it unfair to those big brothers who are already more difficult?
So Yan Shu held up his hand high and reported the situation to Emperor Zhenzong who came to the scene personally: Can you change the topic for me?
True Sect is of course surprised, and what surprises him even more is yet to come. After changing the topic, Yan Shu wrote the article quickly. The key point is that the quality is still very high. It is impressive to write such an excellent article at the age of fourteen.
After such a stunning appearance, Yan Shu officially became a court official. His honest honest and frank left a deep impression on Emperor Zhenzong, so that when the prince (Zhao Zhen played by Wang Kai in Qing Ping Le and later Song Renzong) needed a group of friends to assist him, Zhenzong immediately thought of Yan Shu.
After some inquiries, Zhenzong was even happier: in the Song Dynasty, civil servants advocated carpe diem, and it was common for them to go to the Qin Lou Chu Museum after work. And Yan Shu’s spare time is actually teaching poetry with his younger brother behind closed doors. Isn’t it a blessing for the country to have such a good example around the prince?
This is really a pie falling from the sky. As we all know, as long as the prince can stand, the old people in the prince’s mansion are equivalent to holding a lot of original shares, and the day when the prince rings the bell to practice his position is the time when they reach the sky.
Yan Shu was lucky enough to catch this pie, because of his honest and frank. In the face of the emperor’s praise, Yan Shu once again told the truth: Your Majesty, it’s not that I don’t want to go out for consumption, but I really have no money. When I get rich, I want to be like everyone else …
Yan Shu thought that this pie should be taken back, but I didn’t expect it to be a great joy: honesty and trustworthiness are better virtues than thrift. Love Qing, don’t refuse, and the prince will be in trouble!
Human behavior will be motivated by the environment. Encouraged by the true Sect, Yan Shu should have strengthened his honest and frank attribute, but the complexity of the Korean situation added many variables to the child prodigy’s life.
When Zhenzong died, Renzong was still young, and Empress Liu listened to politics. Empress dowager Liu wants to let Zhang Jian, a favorite, be the Tang Dynasty envoy to take charge of the world’s military affairs. Yan Shu said: How can the state military power be handed over to such a person? I object! So Zhang Jian became a Tang Dynasty envoy, and Yan Shu was demoted.
Empress Liu, stills of Qingpingle
Empress dowager Liu is going to visit the ancestral temple and chat with the ancestors. Immediately, an apple polisher jumped out and said that the queen mother had made great contributions to the little emperor’s country and should wear a grand crown according to the emperor’s specifications. But Yan Shu said, "Your Excellency, this is to give the Queen Mother an early warning, which is not stipulated in the textbook. I object!"! So Yan Shu was demoted again.
Many people study Yan Shu and often get confused. Why is it that this book says that he is "gifted and handsome" and "has great achievements in establishing the dynasty", and that the book says that he is "slick in official positions" and "smooth in dealing with the world"? Don’t you have to use the same caliber to evaluate historical figures?
In fact, there is no contradiction between being strong and handsome, but the former is a sad footnote to the latter. In life, there is no personality that is unchangeable and eternal. Life will teach us many things that we used to sneer at. Our weaknesses will decrease day by day, while our armor will thicken, and an abacus will ring day and night in our hearts, helping us to seek advantages and avoid disadvantages until we are completely different from ourselves when we set out.
Ouyang Xiu, Yan Shu’s favorite pupil, wrote an elegy of Yan Yuan’s offering to the public after Yan Shu’s death. There are two sentences in it: You have been traveling with wealth for 50 years, and you have always kept yourself sane. To preserve our sanity is indeed the key word in the second half of Yan Shu’s life, but the word "always" is obviously biased. We can only blame Ouyang Xiu for coming out too late and missing the scene of his young teacher Geng Jie.
Yan Shu once recommended Ouyang Xiu as an admonition officer after paying homage to the Prime Minister, whose main duty is to supervise by public opinion. As a man who brought his own Italian gun, Ouyang Xiu wrote a letter to show no mercy to dignitaries from all walks of life. Although these were just acts of applause from the people, they were repeatedly severely reprimanded by Yan Shu. Later, Ouyang Xiu was finally persecuted and demoted, but Yan Shu sat idly by. In a word, he is on high alert for anything that may endanger his power.
How can such a person who only cares about his wealth and romance and does not care about the well-being of the whole life dominate the world?
Although Ouyang Xiu not only wrote poems to mourn Yan Shu’s death, but also personally wrote Yan Shu’s Tombstone inscription (similar to the epitaph), it goes without saying that there was disagreement between them. Some Song people’s notes even have a nose and eyes to deduce all kinds of vivid details, saying that Yan Shu commented on Ouyang Xiu in public: I rebuilt the article and didn’t value others. Ouyang Xiu is also not polite: Yan Gong’s small words are the best, followed by poetry, and prose is second to poetry, and he is second to Wen Ye.
Ouyang Xiu, stills of Qingpingle
In a complex situation, it is often only one step away from being wise and being vegetarian or even in cahoots with the corpse. Yan Shu’s way of being an official not only made Ouyang Xiu, a student, condescend, but even Fu Bi, Yan Shu’s son-in-law and a famous minister, couldn’t stand it. On one occasion, he even made a direct statement in front of Emperor Renzong at the court: Extremely treacherous, the party is simple and deceives your majesty! Yan Shu is a wicked villain. He colluded with Lv Yijian to deceive your majesty! )
To be fair, Yan Shu’s personality image is somewhat bleak because of Ouyang Xiu and Fan Zhongyan. How to choose between personal safety and justice has been a completely different answer since ancient times. You reap what you sow, and you reap what you sow. What kind of choice you make must bear the corresponding historical evaluation.
But let’s not forget one thing: Ouyang Xiu, Fan Zhongyan, Fu Bi, Han Qi … These "temporary sages" are all famous in politics with the help of Yan Shu. Although in Yan Shu’s view, these people love to make trouble for him, birds of a feather flock together, so it is no accident that so many famous ministers and sages gather together.
In addition, although he enjoyed wealth all his life, Yan Shu was also famous for his frugality. Needless to say, the most famous thing happened after his death.
After Yan Shu’s death, a group of grave robbers targeted the tomb of the prime minister. They took great risks and made great efforts to dig up Yan Shu’s grave, expecting to return with full load. As a result, they were all dumbfounded: the grave was full of all kinds of earthenware, and there were few valuable things at all.
These people were so popular that they grabbed the knife and axe and smashed Yan Shu’s remains to pieces.
02
Fan Zhongyan, who died in Ning Ming but was born in silence.
If Yan Shu’s historical image is a little split, then Fan Zhongyan is almost a perfect man.
In China, The Story of Yueyang Tower is a household name, and the spirit of "worrying about the world first, and enjoying the world later" can be called the personality model of ancient intellectuals. It’s just that virtue and literature are outstanding. It’s just that this person is still a government official (deputy prime minister), and the "Qingli New Deal" has a great reputation and made great contributions to the fight against Xixia. The three immortals mentioned in Zuo Zhuan-establishing morality, making meritorious deeds and making statements-have been immortalized by many people only by doing one of them, and Fan Zhongyan has covered all three options!
It’ s so arrogant.
Fan Zhongyan, stills of Qingpingle
Although speaking of wealth, Fan Zhongyan may be slightly inferior to Yan Shu, but when it comes to personality charm, Fan Zhongyan has properly dumped several streets in Yan Shu. It goes without saying that the spirit of "Worry first, then be happy" sets an example for later generations. honest and frank is also a sharp weapon for Fan Zhongyan to suck powder.
Fan Zhongyan is two years older than Yan Shu, but he has always been a disciple of Yan Shu, because the foundation of his career was given by Yan Shu (no way, Yan Shu debuted too early). Under the recommendation of Yan Shu, he became an executive of Yingtian Academy, his alma mater, and also got a promising position as a school manager of Secret Pavilion.
Perhaps from the habit of Ouyang Xiu, Fan Zhongyan is also particularly good at making surprises. He has just been promoted to the position of the secret cabinet school manager by Yan Shu, and his backhand has caused Yan Shu a terrible trouble.
When Zhenzong died, Renzong was young, and Empress Liu came to power. As a result, the feeling of reigning over the world was so wonderful that Empress Dowager Liu couldn’t extricate herself. Not only did she not let Injong lead the government, but she also put on a big shelf and let Injong squeeze among the officials to celebrate her birthday.
Of course, it’s normal for a son to celebrate his mother’s birthday, but where is the regal power if the emperor and the officials are in the same column? This is obviously against the rules! Fan Zhongyan was angry, and a righteous and stern paper was presented to the ban.
Before the queen mother responded, Yan Shu was scared to pee first. You know, in the officialdom of the Song Dynasty, recommending others to be officials was jointly and severally liable.
Yan Shu quickly called Fan Zhongyan over and scolded him: This is all the leftovers from Lao Zi’s play in those days, so don’t go fishing for fame in the future!
Fan Zhongyan and Yan Shu, stills of Qingpingle.
To Yan Shu’s surprise, Fan Zhongyan not only did not change his mind, but also wrote a letter to "argue irrationally": I trusted the sage’s book, learned from the ancients’ trip, and was sincere to the monarch and the people … To sum up, what’s wrong?
Fan Zhongyan’s red-faced argument probably reminds Yan Shu of himself when he was young. According to historical records, instead of pursuing Fan Zhongyan’s fault, Yan Shu felt ashamed and apologized to Fan Zhongyan.
Fan Zhongyan is even more confident now. If you don’t stop, it’s a trivial matter for the queen mother to violate the ceremony. The queen mother has been slow to let Injong lead the government. This is the biggest problem! So he waved his hand again, and made another message: Please step back and return the power of governing the country to your majesty!
Everyone was shocked. If the letter in front of me just smoothed the tiger beard of the queen mother, this time it was simply a direct touch on the tiger ass of the queen mother! I haven’t encountered such a thing since Empress Liu listened to politics! If there were media at that time, the headlines of the major media on that day should be: shock! Someone has made such a request to the queen mother …
Although many civil and military officials secretly respect Fan Zhongyan as a man, obviously no one will stand up and support him.
After the throne was handed up, the queen mother did not directly launch a mass destruction to take revenge, but Fan Zhongyan soon felt that he seemed to have broken into the array of nothing and could not stay in the capital completely.
In this way, Fan Zhongyan, who is 41 years old, invited himself to be released as a judge in the river mansion (now Yongji, Shanxi Province), far from the power center of the Dasong Empire, and his future seemed bleak.
Laozi said: misfortune is where happiness depends, and happiness is where disaster lies. Asking the queen mother to return to power angered the queen mother, but made another person praise Fan Zhongyan. This man is naturally Emperor Injong.
Fortunately, Empress Dowager Liu, who is in her twilight years, can’t live forever, while Emperor Renzong is rich in spring and autumn.
Three years later, Empress Liu died, and Fan Zhongyan’s good day came.
Fan Zhongyan was recalled to the court by Injong and became a glorious remonstrator. His job was to give advice to the court. As a result, one of his opinions made Injong fall into a myth.
After the death of Empress Dowager Liu, Injong carried out a wave of political liquidation of the Empress Dowager Party, and a large number of senior officials, including Yan Shu, were removed from their posts. Once every emperor was a courtier, Renzong needed to build his own team.
But in the process, some speculators saw that it was profitable and attacked the late Empress Dowager Liu. Injong was very happy at first: great! They are all loyal ministers! Prepare to give these people a promotion and a raise.
Fan Zhongyan hit the nail on the head: do you think these people are really loyal to your majesty and indignant at the queen mother? Why didn’t they say a word when the queen mother was alive? The queen mother may have many faults, but she still made great contributions to the country, but she can’t be killed with a stick!
It is undoubtedly a great risk to speak well of the queen mother at this time. Fortunately, Renzong didn’t show great anger, but accepted Fan Zhongyan’s suggestion generously, and issued a letter forbidding ministers to talk nonsense about the queen mother’s past affairs.
If Injong had a steelyard in his heart, he should have understood at this time that this guy named Fan Zhongyan, in every word and deed, focused on the country and the world, demanding that Empress Dowager Liu return to politics and maintain Empress Dowager Liu. It seems contradictory, but it is actually the same principle. Renzong’s affection for Fan Zhongyan increased again. Fan Zhongyan’s ability to participate in political affairs and preside over the Qingli New Deal all the way is inseparable from Renzong’s recognition of him.
Many people are passionate when they are young, and they have encountered many nails. When they are older, they learn to share the same dust and protect themselves. To put it bluntly, it is to put the home country and the world after the personal name. Fan Zhongyan is not. He seems to be young forever, always full of heart. He is like an annoying crow in the face of current abuses and treacherous officials’ evil policies: Ning Ming died and was born silently.
Stills of Qingpingle
Later, Renzong wanted to abolish the Queen Guo, and the Prime Minister Lv Yijian and the eunuch leader Yan Wenying were in trouble. All these things made Fan Zhongyan stand up and speak out, even though he was repeatedly denounced, he still didn’t change his mind.
When it comes to Fan Zhongyan’s career, fighting Xixia is second to none. In fact, in this matter, Fan Zhongyan suffered many criticisms because he was too opinionated.
At that time, the Da Song Dynasty was in its prime of life and full of vigor and vitality. Faced with Xixia’s provocation in the frontier, there were shouts and beatings from top to bottom, and they all wanted to make a quick decision and promote China’s prestige (in sharp contrast to the Southern Song Dynasty after the Jingkang Revolution).
However, after a calm analysis, Fan Zhongyan pointed out: the dispatch of a large army is related to the lives of millions of people, so we must be cautious. The fighting capacity of Xixia Army is stronger than that of Song Jun, and active defense is the way to win. Specifically, it is impossible to stick to it and prevent the front from being hard and rigid. When necessary, you can even send a bunch of "old coins" to Xixia every year, just like the Khitan, and exchange money for peace.
As one of the handsome men in the northwest, it will obviously be despised by the time theory to throw out such a timid idea. In the spring of 1041, Song Jun finally drew his sword and raised his crossbow, ready to fight Xixia to the death.
Before the war, Xia Song, the head coach, sent someone to lobby for 20 days, and asked the court Commissioner to supervise Fan Zhongyan’s invasion. Finally, Fan Zhongyan still chose to stay put.
In the eyes of contempt, Fan Zhongyan and others came to the news of Song Jun’s crushing defeat.
More than 10,000 people were killed, and a large number of counties and counties were burned, killed and looted. Fan Zhongyan, who didn’t send troops, also received a letter from Li Yuanhao, the Lord of Xixia Kingdom, whose tone was arrogant and arrogant. If Emperor Renzong saw it, it would be a great shame. Fan Zhongyan had to make his own decision, set the letter on fire, and only selected the part with gentle tone to play in the court.
After this battle, Fan Zhongyan’s strategic thought of active defense was finally popularized in the northwest border. Although this is not powerful enough, the curative effect is extremely remarkable. With the joint efforts of Fan Zhongyan and his good friend Han Qi, the northwest border has gradually become impregnable. Although the Xixia army died in my heart, it failed to get much cheaper.
The northwest people are grateful to Dade and wrote the following ballads: there is a Korean in the army, and the western thieves are frightened when they hear it; There is a school in the army, and the western thieves are shocked by it.
In the end, Xixia, a small country and poor people, could not bear the huge consumption caused by successive years of war, and its economy collapsed, so it could only make peace with Dasong. Fan Zhongyan defeated the enemy without fighting and was promoted by Renzong to participate in political affairs.
Although the northwest frontier fortress made Fan Zhongyan make contributions to the peak of his life, he obviously rejected the ominous thing of war.
Why don’t men take Wu Gou and collect fifty states of Guanshan (Li He)? Many poets and scholars are full of magnificent and romantic imagination about frontier fortress and war. As a frontier commander, Fan Zhongyan left a poem "Fisherman’s Pride Qiu Si", which is neither burning nor positive energy. After reading it, it will only make people frown and ponder.
The scenery in Qiu Lai is different, and Hengyang geese go unnoticed.
The four sides are connected with each other. Thousands of miles away, the long smoke and the sunset are closed.
A glass of turbid wine is home to Wan Li, but Yan Ran has not returned home.
Qiang Guan is covered with frost. People are sleepless, and the general has white hair and tears.
Fan Zhongyan, stills of Qingpingle
03
Ouyang Xiu, who is full of peach news.
Compared with Fan Zhongyan’s perfect image, Ouyang Xiu’s political integrity is also praised, but his private life and ci creation are a bit complicated. He seems to bring his own black physique, and being hacked into Xiang is just a starting price.
Zuiweng Pavilion is an article that all students in China can recite. How popular was this article after it was published?
It is too conservative to describe Luoyang paper as expensive. The rubbings of The Drunken Pavilion were carried by unscrupulous traders. Every time they passed through a checkpoint, they had to pay taxes. The traders called the tax collector to a secluded place to give him a copy, and the other party was ecstatic and let him go!
When talking about the creative background of The Drunk Pavilion, the Chinese teacher will surely tell you that Ouyang Xiu, because of his honest and frank temperament, criticized the shortcomings of the times for three days and joined Fan Zhongyan’s "Celebration New Deal", which offended many dignitaries, so he was greedy and demoted, and wrote this masterpiece in Chuzhou.
However, the problem comes: although the routine of political struggle has always been used as an excuse, there must always be a specific charge for punishing cadres, right?
For example, Su Shi’s demotion to Huangzhou is a poem that satirizes the current politics, Han Yu’s demotion to Chaozhou is an admonition to meet the Buddha’s bones, and his words are too ugly. Liu Zongyuan and Liu Yuxi are due to the failure of Yongzhen’s innovation and the fall of his eldest brother. What is the charge of Ouyang Xiu’s demotion of Chuzhou?
The answer may surprise you: incest. Ouyang Xiu was accused of having an improper relationship with his niece Zhang.
Zhang is the daughter of Ouyang Xiu’s sister’s ex-husband (so strictly speaking, she is not related by blood) and was fostered in Ouyang Xiu’s home when she was a child.
Because of her beauty, she is affectionate. After marriage, Zhang committed adultery with his servant and was sent to the government by her husband.
Originally, it was a small case, but when Kaifengfu Yin stumbled upon it, the derailed love rat turned out to be Ouyang Xiu’s niece and lived in Ouyang Xiu’s house for several years, and his eyes shone blue. Headed by two prime ministers, people who were unhappy with Ouyang Xiu smelled bloody sharks and quickly gathered around the case. They were as fierce as a tiger, taking mitigating punishment as bait, threatening Zhang to throw a basin of sewage at Ouyang Xiu.
Aren’t you healthy and upright? I thought you hated evil. Come on, take off your pants and show everyone how dirty your ass is!
The peach news of celebrities is already eye-catching, let alone with their nieces! For a time, public opinion was boiling, and the ruling and opposition parties were in uproar. The hot search list was paralyzed several times.
However, from the beginning to the end, there was only Zhang’s one-sided story, which was still a thing of the past. How to win the trust of others?
Unexpectedly, a small word written by Ouyang Xiu many years ago became the most powerful evidence.
Willow in the south of the Yangtze River, the leaves are small and not overcast.
Man-made silk is light and forbearing to fold, and the warbler thinks the branches are tender and cannot be sung. Save it for the spring.
Fourteen-five, leisurely holding the pipa.
Go up the stairs and down the stairs, and be careful when you meet each other. Besides, by now. ("Looking at Jiangnan")
I have to admit, this word is really a bit obscene. Let people see such a scene: a greasy old man, flirting with the little girl’s hand: beauty, I have been paying attention to you for a long time!
It really doesn’t make sense if nothing happens between them.
Fortunately, this kind of thing was too difficult to obtain evidence in ancient times, and in the end, it could not be convicted. Ouyang Xiu’s political career was not devastated. With a dirty water, hastily demoted out of the capital.
The above is the complete creative background of Zuiweng Pavilion.
A man was in a body wash, but was accused of incest. This shows that his enemies are really shameless.
But what does it mean if a person is accused of incest twice when he is in the toilet?
Ouyang Xiu, stills of Qingpingle
Ouyang Xiu, who has spent years in luxury and is a deputy prime minister, never imagined that a bigger basin of sewage was brewing and gathering in an inconspicuous corner.
Things are still caused by a relative (you see, relatives have been enemies of many people all their lives). Mrs. Ouyang Xiu’s cousin Xue Liangru recommended a Beijing official to the court when she was a doctor in the Ministry of Water Resources. Didn’t chengxiang, this guy caught the graft, causing Xue Liangru to be jointly and severally liable, and his job was in jeopardy.
At first, Xue Liangru had nothing to hide: Lao Tzu’s brother-in-law is the deputy prime minister, what can this little thing do to me! Ouyang Xiu made it very clear: The more leading cadres, the more they should set an example. Relatives, let’s follow the procedure.
Xue Liangru, who was found guilty of losing his official position, was furious: I don’t know you yet! Tell people everywhere: Ouyang Xiu is a big slut! Don’t even let your daughter-in-law go!
If Zhang is only Ouyang Xiu’s niece in the legal sense, his daughter-in-law Wu is his "biological" daughter-in-law!
National leaders+top celebrities+incest ×2. If you convert it, what a battle this news will be.
Since public opinion has been widely fermented, the discipline inspection department will follow up. Ouyang Xiu suffered the most horrible crisis since he entered politics. No matter what the final investigation results are, they have been ruined and swept the floor.
Why is Ouyang Xiu’s life style always talked about?
Flies don’t bite seamless eggs. It’s time to know how wild Ouyang Xiu’s lyrics are.
Ouyang Xiu wrote a lot of books all his life, and only wrote lyrics, leaving many well-known famous sentences: tears asked flowers and flowers without words, and red flew over the swing. The moon rose above the willow tree, At dusk he had a tryst with me. Ah, there is love in life, love in the depths of the crazy, this is not to hate not related – the head of the wind, the moon in transit.
Affectionate, simple and beautiful.
However, in Ouyang Xiu’s ci collection, there is another kind of words that often make later researchers blush and feel like deer bumping into each other. Some people even tore the book and lifted the table in anger: impossible! How can this be written by Ouyang Wenzhong! Some bad guys forged it to ruin his image! Can we delete all these things from unknown sources?
As a matter of fact, it is a common ethos for literati in Song Dynasty to enjoy life and indulge in debauchery, especially Ouyang Xiu, who is a good player. There is no need to cover up the shortcomings of great men. No matter how great the personality is, it also has its vulgar side.
At that time, Ci was mainly used to add fun to songs and banquets, so I loved to write "the state of beautiful Luo Xiang Ze, the posture of saving for a rainy day." It is not difficult to understand that men and women are deeply attached to sex and obscenity, and the style and moral integrity are smashed and scattered all over the floor.
So, how wild is Ouyang Xiu to write such words?
Take a look at the following song "Nanxiangzi":
Good person, deep lips and light cheeks.
Meet under the flowers, busy and afraid of guessing. Left a bow and small embroidered shoes.
Hmm (ch ǐ n) socks come back, and half a day (duǒ droops) clouds and golden hair.
Laugh and laugh, hug and touch each other. Simple and naive has always been reluctant.
What a beautiful person, her lips are red and her cheeks are pale. Encounter and meet, afraid of people gossiping, leaving me only a small curved embroidered shoe. Disappointed, she ran back wearing only socks, with a cloud of hair and a golden hairpin. We laughed and hugged each other tightly, and she stuck in my arms and could not leave.
How about it? Is it very different from the Song Ci you usually read? Do you think that writing about the love between men and women is such a firm and pure feeling that "the clothes are getting wider and wider and you will never regret it, and you will be haggard for Iraq"? Do you think the description of lovers’ dating is so subtle and beautiful as "a curtain of dreams in jathyapple, ten miles of tenderness in the spring breeze"?
It can also be disgusting and shy, which is not suitable for children.
If you don’t believe me, let’s take a look at the following song "Yi Qin E":
Fifteen, six, take off the petticoat, long and graceful (nèn is so) and frown.
Ruby is warm, enters people’s arms, and is ripe in spring.
Show incense (y and n clothes), and draw candles in front of the account.
Eye wavelength, inclined to soak the temples in cloud green. Not enough.
Bitter night, more missed.
Is the picture strong? Is there much action? Dawn is too early, and love is not enough for one night. Bai Juyi also wrote this meaning: but nights of spring were short and the sun arose too soon, and the Emperor, from that time forth, forsook his early hearings. By comparison, Ouyang Xiu’s writing is really wild …
Including the song "Looking at Jiangnan" quoted earlier, I read a sentence about the central idea: This author has no good intentions!
What kind of experience is it to be a deputy prime minister but always write such little yellow poems? For example, if you take off the shirt and suit of a president of a fighting nation, you find that there is still a Chinese-style chest covering inside, and the pattern on the Chinese-style chest covering is still … a playboy version of a beautiful girl warrior.
No wonder there are always people staring at Ouyang Xiu, who are ready to blame him for the relationship between men and women-as the saying goes, if you write words like this, you can’t go into the sea!
Stills of Qingpingle
What’s even more cool is that it’s no better than corruption and buying and selling officials. Although I can’t catch you, I can disgust you to death. Although I can’t get hard evidence of your incest, you can’t get hard evidence of your incest, can you?
In the case that Xue Liangru slandered Ouyang Xiu for incest with his daughter-in-law, there was no winner. After some investigation, the then emperor Song Shenzong (Injong left no children, Yingzong was his adopted son, and Shenzong was the son of Yingzong) decided that the matter was false and banished the officials who contributed to it from Beijing. However, the humiliation and cyber violence suffered by Ouyang Xiu and his family are irreversible.
Ouyang Xiu, who is disheartened, is determined to stay away from right and wrong. He voluntarily resigned from the post of deputy prime minister, and went to a lonely province to be an official.
The legal retirement age in the Song Dynasty was seventy. But Ouyang Xiu was tired of this cheating and backstabbing officialdom. At the age of sixty-five, he took early retirement.
At that time, no one understood. After all, the biggest fear of a man who is a second-rate official like him is that people leave tea cool. Giving up high officials and high salaries in advance is "unheard of in the past century."
Only Su Shi, the first disciple of Ouyang Xiu, congratulated the teacher. Only he knows that this seemingly hale and hearty old man has been in the sewage for too long, and it’s time to throw his head away from the open fire and stab in the back. It’s time to go back to the original starting point and live a clean life.
Many people wonder why Ouyang Xiu is so black, and why the moth always lies in the relationship between men and women. You don’t know how straightforward Ouyang Xiu is and how good at offending people.
Just give me an example. Feel it.
As mentioned above, Yan Shu, a great poet who wrote "I feel helpless when the flowers fall, but I feel familiar when Yan returns", is Ouyang Xiu’s mentor. When Ouyang Xiu started his career, Yan Shu was already the highest military officer in China. Yan Shu invited Ouyang Xiu to his mansion to enjoy the snow. When it is beautiful and enjoyable, it is natural to write a poem to help add to the fun and push the happy atmosphere to a climax.
With a stroke of his pen, Ouyang Xiu wrote a long poem of seven words, and the last two sentences read: You must pity the armored soldiers and freeze to the bone, and more than 400,000 troops will be stationed on the border. Teacher, when you were enjoying the snow, thousands of soldiers in Qian Qian were freezing in the frontier!
Click, click, click … Friend, if you were Yan Shu, would you like to cut off Ouyang Xiu’s neck and send it to "Juewei" for marinating, leaving a wonderful flavor for the world? ?
This is still true for teachers, for enemies, and for everything ugly and unreasonable in the world.
Those who have been impeached and offended by Ouyang Xiu want to fight back in their dreams and find evidence of graft from Ouyang Xiu. Unfortunately, all their efforts were in vain, and they were dejected and despondent like defeated cocks. Finally, someone patted his forehead: look at the words written by this guy!
Those small eyes flashing green light finally showed a steep smile.
04
Su Dongpo, who changed from an idol to an abandoned minister.
Great souls probably have their own unique smells, so that they can attract each other and achieve each other.
In the Tang Dynasty, it was Li Bai Du Fu Gao Shi, Han Yu Liu Zongyuan Liu Yuxi, and in the Song Dynasty, it was Yan Shu Fan Zhongyan Ouyang Xiu. Without each other, their lives may be greatly rewritten.
At this point in this article, it is time for Ren Zongchao to appear as the last great talent.
In 1057, a gifted scholar from Sichuan was in a good mood. In the just-concluded national college entrance examination, he won the silver in one fell swoop and won the runner-up in. It is said that after the examination, Emperor Injong cheerfully went to the harem to report the good news to Empress Cao: I have won two Prime Ministers of Taiping for my descendants (the other is Su Shi’s younger brother Su Zhe)!
This future "Prime Minister of Taiping" is Su Shi, the first disciple of Ouyang Xiu.
In that well-known story, Ouyang Xiu owed Su Shi a number one scholar, but he also gave him an idiom: get ahead. Ouyang Xiu also boldly predicted that this young man’s world will be in thirty years, and no one will remember me!
In order to hype Su Shi, Ouyang Xiu was a little too modest.
In 1056, Ouyang Xiu gave a banquet in Beijing and sent a good friend to Yangzhou to be an official. Ouyang Xiu also worked in Yangzhou when he was young, and planted a willow tree in front of Pingshan Hall.
Now that the sun and the moon have passed, the drunkard is old, and only the weeping willows in front of the hall are still glowing, they are tall once more in the spring wind. When scholars send each other, they usually send them away with poems, which are more formal than words. Ouyang Xiu wrote this famous "Chao Zhong Cuo" for his friends:
Pingshan Lansill leans against the clear sky, where the colour of mountains both is and is not.
Plant willows in front of the hall, don’t have a few spring breeze.
My favorite article is the governor of writing, writing is lengthy words, drink a drink to drink.
Take advantage of the young man now, and you can see the old man sitting in front of Bottle.
Twenty-three years later, Su Shi passed by Yangzhou and saw the handwriting of this word in Pingshan Hall. Each stroke carried the teacher’s body temperature.
At this time, Su Shi is no longer the fledgling, fearless lad, and his 43-year-old face has begun to bear the imprint of vicissitudes.
In the DPRK, Wang Anshi’s political reform was in full swing. As an opponent of political reform, Su Shi felt perplexed in the middle of his life.
And he would never have thought that in just a few months, he would usher in the "Wutai Poetry Case" that shook the ruling and opposition parties. This menacing "literary inquisition" will turn him from a local official to a prisoner, from an idol who is lying and sucking powder to a guilty minister who everyone hates.
If the teacher is alive, he will certainly be able to help him shake the clouds and repel the siege of the villain. Unfortunately, "if" is the cheapest comfort in the world.
At the fork in the road of fate, in front of the teacher’s handwriting, Su Shi did not live up to his talent. He used an equally immortal "Xijiang Moon" to pay a sparkling attention to Ouyang Xiu who had disappeared in the depths of the years.
Three times under the Pingshan Hall, half a lifetime of snapping.
I haven’t seen the old fairy for ten years, and the dragons and snakes are flying on the wall.
If you want to hang the article, you will still sing the willow spring breeze.
Needless to say, everything turns empty, and when you don’t turn your head, you dream.
References:
Tuotuo, Arutu, etc., History of Song Dynasty, Zhonghua Book Company, 2017.
Biography of Fan Zhongyan by Zhuge Yibing, Zhonghua Book Company, 2012.
Huang Jinde’s Biography of Ouyang Xiu, Nanjing University Press, 1998.
Kang Zhen’s Kang Zhen on Ouyang Xiu and Ceng Gong, Zhonghua Book Company, 2018.
Shao Mingzhen, On the Deep Causes of Yan Shu’s Stigma, Journal of Suzhou University (Philosophy and Social Sciences Edition), November 2018.
Shao Mingzhen’s Dialectics of Yan Shu’s "Being Wise to Protect Our Body", Research on Literary Theory, March 2019.
Gao Feng’s Bad Relations between Yan Shu and Ouyang Xiu and the Change of Ci Style, Journal of college of nanjing normal university, December 2017.
Fan Zhongyan and Yan Shu by Liu Deqing, Cultural Studies of Song Dynasty, January 2009.
Editor | _ Child _ refers to Xinghua Village
Editor | Wei Bingxin
Picture | Network
Knowledge | Thought | Reading Books and Literature | Interest
Original title: Qing Ping Le: How was the golden age of literature refined? | Peng Min "
Read the original text